In today’s digital world, securing your email is more important than ever. The Ultimate Guide to DKIM, SPF, and DMARC helps businesses and individuals protect their domain from phishing attacks and domain spoofing. These protocols ensure that your emails reach the inbox, improving email deliverability and maintaining a strong domain reputation.
By properly configuring DNS records and adding DKIM signatures, you can authenticate messages and prevent fraud. Whether you are sending marketing campaigns, transactional emails, or personal messages, understanding and implementing these email authentication tools is essential for maintaining trust, protecting your brand, and ensuring smooth communication across all email platforms.
Introduction to Email Authentication
Email authentication is a set of techniques used to confirm that an email is sent by the legitimate domain owner. Without it, anyone can forge your domain and send spam, leading to domain spoofing and phishing attacks. By verifying the sender, email providers can protect recipients from malicious content while improving email deliverability.
For businesses, implementing authentication is a vital part of email security for businesses. It ensures your messages reach the main inbox instead of being lost to the spam folder or blocked entirely. Strong authentication builds domain reputation and protects your customers from fraud. With the right setup, even forwarded emails maintain email alignment and integrity.
Understanding SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is one of the oldest yet most effective protocols. It works by checking the IP address verification of the server sending emails for your domain. If an IP isn’t authorized in your SPF record setup, the message might be rejected or flagged as spam. This simple check prevents spammers from impersonating your domain.
How to set up SPF on your server involves adding a DNS TXT record with all authorized email servers. Common services like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, or Zoho require specific entries. When configured correctly, SPF protects against email phishing protection, and ensures your legitimate emails are recognized by email service providers and reach the inbox.
Understanding DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
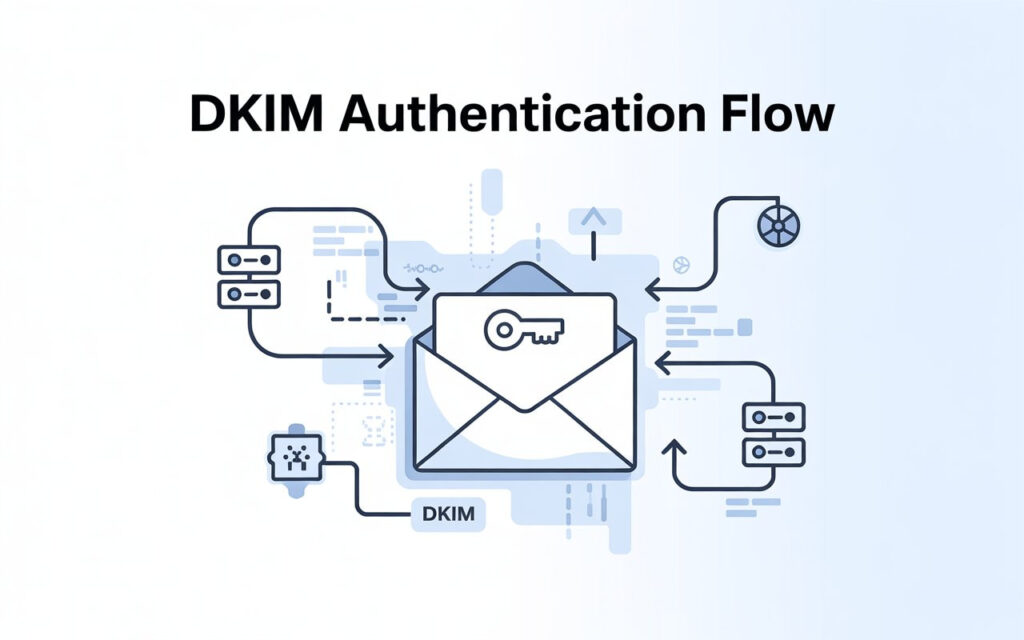
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) adds an encrypted signature to your email headers. This DKIM signature proves that the content hasn’t been altered during transit. When a recipient server checks the signature against your public key in the DNS records, it confirms authenticity. This method adds another layer of email security beyond SPF.
How DKIM improves email deliverability is significant. Emails with valid DKIM signatures are less likely to land in the spam folder and more likely to be trusted by recipients. Steps to configure DKIM and SPF involve generating keys, publishing them in DNS, and activating signing on your email server. Together, SPF and DKIM form a strong foundation for email authentication.
Introducing DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM to give domain owners control over how emails failing authentication are treated. A DMARC policy can instruct servers to quarantine or reject suspicious messages. This helps reduce domain spoofing and protects domain reputation in the eyes of email service providers.
The importance of DMARC for brand protection cannot be overstated. DMARC also allows you to collect insights through reports. Using DMARC report analysis tools, you can see who is sending emails from your domain and adjust policies to improve email deliverability. Implementing DMARC is crucial for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for beginners to maintain trust and reduce phishing risks.
DMARC Policies and Reporting
DMARC offers three main policies: none, quarantine, and reject. The none policy lets emails pass while monitoring, quarantine moves suspicious emails to the spam folder, and reject blocks them outright. These policies help maintain domain reputation and protect against impersonation.
How to read DMARC reports involves checking IP addresses, SPF/DKIM alignment, and email sources. Reports help identify email forwarding issues and potential spoofing attempts. Using this data, businesses can adjust their DNS settings and improve email authentication for higher inbox placement.
Troubleshooting and Best Practices
Troubleshooting SPF, DKIM, and DMARC requires checking DNS records, alignment, and policies. Common mistakes include missing SPF entries, incorrect DKIM keys, or misaligned domains. Regular monitoring is essential to maintain email security for businesses and prevent emails from being flagged.
Best practices for email authentication include keeping your DNS records updated, using strong DKIM keys, and monitoring DMARC reports. Aligning SPF and DKIM correctly ensures email alignment. Avoid shortcuts; small misconfigurations can hurt email deliverability and brand credibility.
Improving Email Deliverability
Email deliverability depends on proper authentication, content quality, and sending reputation. Aligning SPF and DKIM reduces bounce rates and prevents emails from being marked as spam. A verified DKIM signature and a valid SPF record show email service providers that your domain is trustworthy.
Businesses should also monitor engagement and avoid sudden spikes in volume. Using authentication protocols alongside clean lists improves domain reputation. Regular checks for email headers, IP address verification, and email encryption further enhance deliverability. Over time, these steps build long-term trust and inbox placement.
Case Studies & Real-World Scenarios
A small US business noticed customers weren’t receiving newsletters. After implementing SPF and DKIM, their emails reached 95% of inboxes. Adding DMARC later prevented phishing attempts using their domain. Another company fixed misconfigured SPF records, drastically reducing emails landing in the spam folder.
These cases show the practical value of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for beginners and advanced users. Monitoring reports and maintaining domain reputation ensures long-term email success and robust email security against spoofing.
FAQs About SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
The main differences between SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are in their methods of authentication and enforcement. SPF checks sending servers, DKIM validates email encryption in headers, and DMARC defines policy for failed messages. Using DNS TXT records for email security ensures alignment and improves trust.
Businesses should review records periodically, check reports, and maintain proper email alignment. Common mistakes in SPF and DKIM setup include missing servers, expired keys, or misalignment. Tools for DMARC report analysis help identify and fix these problems efficiently.
Conclusion & Next Steps
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are essential for any business concerned with email security, email deliverability, and domain reputation. Setting up these protocols prevents spoofing, enhances trust, and ensures emails reach the inbox.
Next steps include checking current DNS records, configuring SPF and DKIM, and gradually enforcing a DMARC policy. By monitoring reports, resolving alignment issues, and following best practices for email authentication, your domain remains secure, reliable, and respected.
Stop Emails From Landing in Spam
LeadsMonky · Trusted by 500+ B2B companies
FAQs
Q: How to setup SPF, DKIM and DMARC?
A: Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC in your domain’s DNS to authenticate emails and prevent domain spoofing.
Q: What is an SPF, DKIM and DMARC checker?
A: It’s an online tool that verifies if your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are correctly set and aligned.
Q: How to setup SPF, DKIM and DMARC in Office 365?
A: Use the Microsoft 365 admin center to add SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for secure email authentication.
Q: What is SPF, DKIM, and DMARC?
A: They are email authentication protocols that prevent phishing, improve email deliverability, and protect your domain reputation.
Q: A beginner’s guide to SPF, DKIM and DMARC free?
A: Free guides show step-by-step instructions to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for stronger email security.
Q: How to setup SPF, DKIM and DMARC in GoDaddy?
A: Add SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records through GoDaddy’s DNS management to secure your domain’s emails.



